What is Dental Caries/Tooth Decay?
Tooth Decay is caused by a breakdown of the tooth enamel. This breakdown is the result of bacteria in the oral cavity acts on the foods and produce acid that destroys tooth enamel and results in tooth decay.
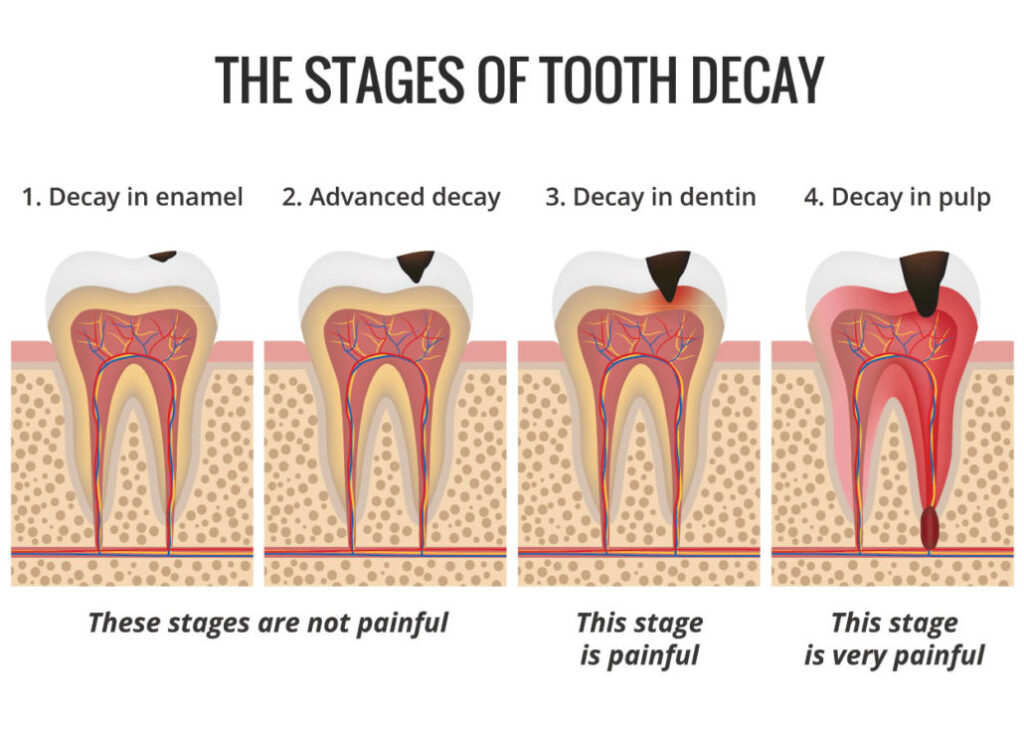
How to identify tooth decay?
- Brown, black or white staining on any surface of a tooth.
- Visible holes or pits in your teeth.
- Toothache, spontaneous pain or pain that occurs without any apparent cause.
- Tooth sensitivity.
- Mild to sharp pain when eating or drinking something sweet, hot or cold.
Treatment options for tooth decay!!!
Depending upon stage of the disease
Dental Fillings: if the tooth decay progressed to enamel and dentin
Fillings are the most common form of treatment for the disease. Dentist will drills into the affected area(s) of the teeth, removes the decayed material inside the prepared cavity, and packs this empty space with an appropriate dental filling material.
Various filling material available: Depending upon the need of the Patient material of choice will be selected
- Silver Amalgam
- Glass Ionomer Cement (GIC)
- Composite
Root canal treatment (RCT): if decay progresses to pulp and tooth can be restored.
As tooth decay progresses through the enamel and dentin, it may even advance further and damage the nerves, which are in the root. A dental professional would remove the damaged or dead nerve with the surrounding blood vessel tissue (pulp) and fill the area. The procedure usually ends with the dentist placing a crown over the affected area.
Extraction (Removal of tooth): if tooth cannot be restored.
Dentist will anaesthetize the area where decayed tooth is present and remove the tooth with specially designated instruments and will place suture if required. This procedure has to be followed by placing bridge or implant in the region of removed tooth to maintain functionality and aesthetics.
How to prevent dental caries?
- Proper oral hygiene maintenance.
- Proper brushing technique and Fluoridated tooth paste– 2/day.
- Flossing regularly.
- Balanced diet and limited snacking.
- Regular dental visits –once in every 6 months.
- Topical fluoride application and pit and fissure sealants.
